Open Data #1: Basic Understanding
Open Data #1: Basic Understanding
The disclosure of government data has become one of the key topics widely discussed and continuously implemented over the past several years. Open Government Data plays an important role in enhancing transparency, improving public services, and supporting data-driven policy development. In Thailand, three key organizations have been working collaboratively to drive all 20 government ministries toward strengthening and improving the Government Data Catalog. These organizations include: Digital Government Development Agency (DGA) National Statistical Office (NSO) Office of the Public Sector Development Commission (OPDC) This collaborative effort aims to establish a standardized and integrated government data ecosystem, enabling effective data sharing, accessibility, and utilization for the benefit of the public sector, private sector, and society as a whole.
Simply Bright System Co., Ltd. has had the opportunity to develop Open Data systems for a wide range of organizations across both the public and private sectors. Based on this experience, the company initiated the development of a series of articles to provide guidance on Open Data Platform development, as well as approaches for effectively utilizing open data to create further value and innovation. This article serves as an introduction, beginning with key definitions and terminology related to Open Data to establish a clear and common understanding. More in-depth technical and implementation details regarding Open Data system development will be presented in subsequent articles.
Definition of Open DataOpen Data refers to data that is freely available for everyone to use, reuse, and redistribute without restrictions. There are no limitations on the type or domain of data that can be published as Open Data. Any organization or agency can disclose data they collect, including but not limited to: Personnel data Budget and financial data Geographic and spatial data Climate and environmental data Indices and key performance indicators Reports and analytical documents Typically, Open Data is published in the form of datasets. Each dataset consists of two main components: Metadata – descriptive information that explains the dataset Data Resources – the actual data files available for access and use In some organizations or systems, a Data Dictionary may also be provided to describe the meaning of each data field in detail. This helps users correctly interpret and effectively utilize the data.
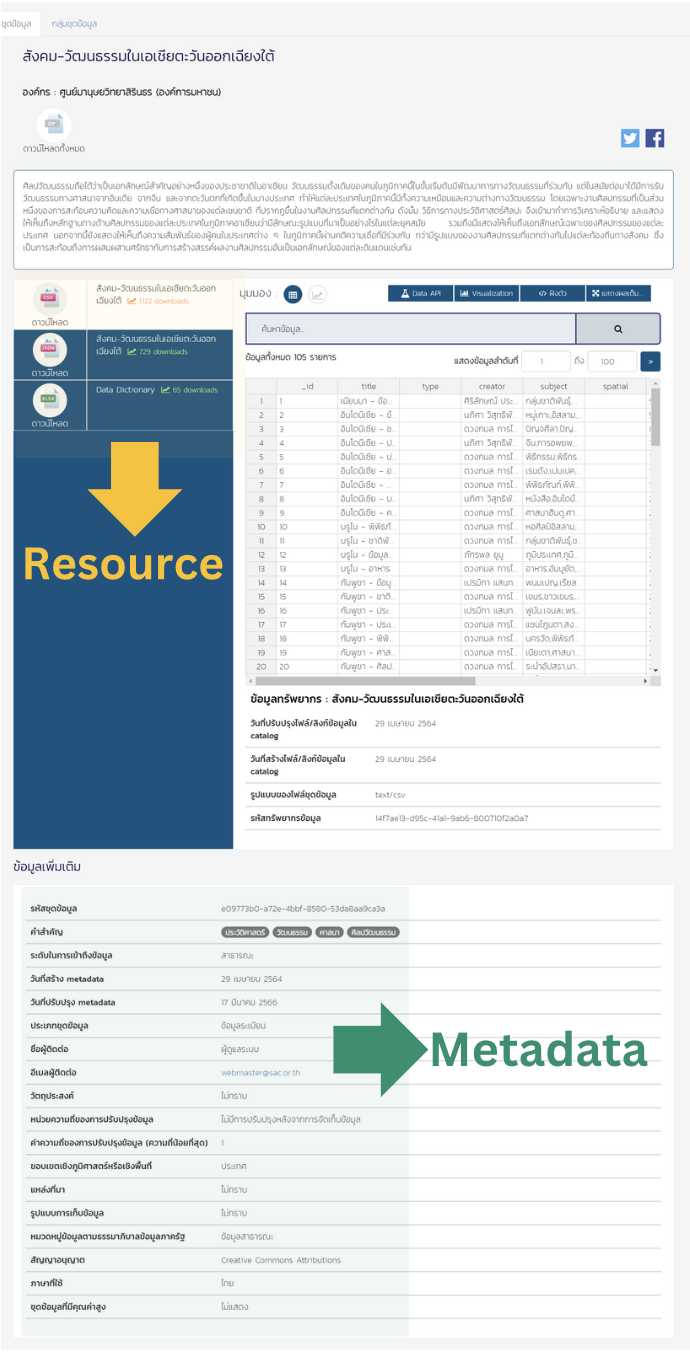
Metadata refers to descriptive information that explains the background and characteristics of a dataset. It provides essential context that helps users understand, discover, and correctly utilize data. Metadata typically includes details such as: Dataset title Data-owning organization Responsible person or unit Keywords Description Objectives Data source Data format and storage method In Thailand, the Digital Government Development Agency (DGA), in collaboration with the National Statistical Office (NSO) and the Institute for the Promotion of Big Data Analytics and Management for Government (GBDi), has developed a minimum metadata standard. This standard is based on ISO/IEC 11179 and the Dublin Core Metadata Initiative (DCMI), along with standardized document templates. These standards define the metadata structure for government datasets, enabling public sector agencies to consistently and systematically develop their data catalogs. Government data has been categorized into five data types, each sharing 14 core metadata elements. Additional metadata elements may be required depending on the specific type of data.


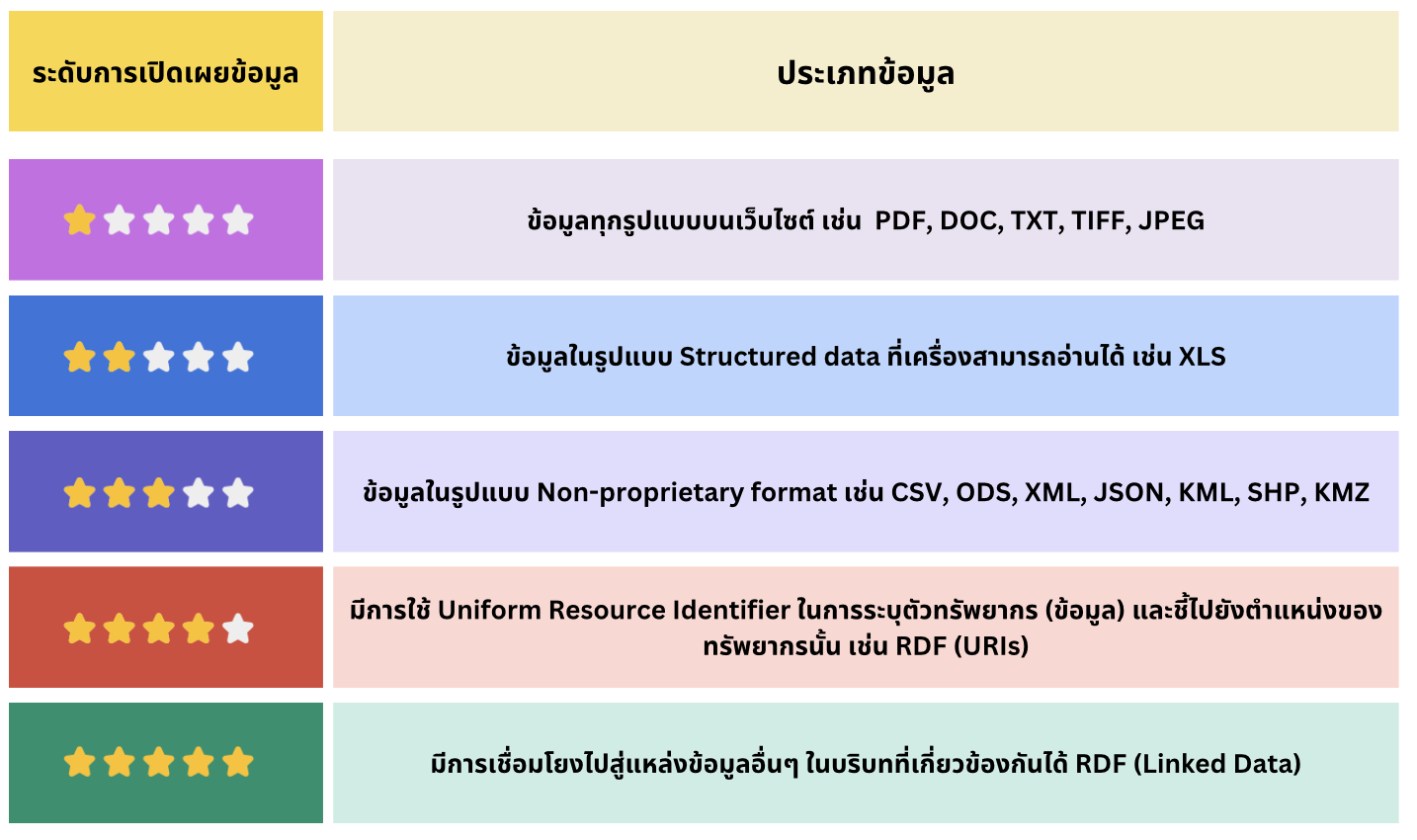
Data Resources refer to the actual data files that are published and made available for use. Government agencies and organizations can disclose data they collect in various file formats, depending on the nature and purpose of the data. Commonly published formats include, but are not limited to: DOC XLS PDF JPEG CSV RDF The choice of file format should support accessibility, usability, and reusability for different types of users. In addition, the Digital Government Development Agency (DGA) has defined five levels of data openness to guide government agencies in publishing data appropriately. These levels help determine the degree of accessibility and reusability of data, ensuring alignment with national open data policies and standards. https://www.dga.or.th/document-sharing/article/35847/
Data Catalog Another frequently mentioned term in the context of Open Data is Data Catalog.
By definition, a Data Catalog is a structured listing of all datasets owned by an organization. These datasets are grouped or classified according to categories defined by the data-owning agency. The datasets listed in a Data Catalog may include both open data and restricted (closed) data, depending on the policies and decisions of the data owner. A Data Catalog serves as a central reference that enables organizations to manage, discover, and govern their data assets effectively, while also supporting transparency and data-driven decision-making.
In addition, the Digital Government Development Agency (DGA), the National Statistical Office (NSO), and other related agencies have provided official definitions, recommendations, and practical guidelines regarding Data Catalog implementation. These resources are available through various channels for further study, including:
- Digital Government Development Agency (DGA): https://www.dga.or.th/document-sharing/infographic/60945/
- Thailand Open Government Data Portal: https://data.go.th/pages/about-open-data
- National Statistical Office (NSO) Help Page: https://gdhelppage.nso.go.th/p06_02_04.html
- NRCT Data Catalog FAQ: https://catalog-data.nrct.go.th/faq